Evolution Of Clinical Data Management: An indispensable part of the healthcare industry, Clinical Data Management is integral to clinical trials – a critical tool in improving human health and bring forth medical interventions that can elevate the quality of life for everyone.
In this blog, Learning Labb Research Institute will take you on a journey to the early days of clinical data management (CDM) and the evolution of clinical data management that has paved the way for several development in the healthcare field.
This article contains the following:
- Evolution Of Clinical Data Management (Overview)
- History Of Clinical Data Management
- Clinical Data Management Modernization
- Digital Transformation Clinical Data
Evolution Of Clinical Data Management
The importance of data cannot be overstated, every other aspect in today’s world is motivated by data. Data is used in decision making, research, and product development -central to gain insights into customer behaviour, trends, and predictions. The way our life is consumed by data is indeed commendable.
It is important to point out that Clinical Data Management (CDM) is a important process in CR, so is it within a clinical research course, where as the same applied in generating high-quality, reliable, and statistically sound data from clinical trials. CDM ensures the collection, integration, and availability of data, maintaining the necessary quality and cost-effectiveness throughout the process.
One such crucial data is the data that we all owe our existence to (in a way) – Clinical Data. Clinical data is the collection of data related to the patients, including patient diagnosis, demographics, exposures, laboratory tests, and family.
The evolution of clinical data management since the early 1920s has seen a steady growth and has undergone transformations that has altered the medical field immensely. Let us take you on an expedition through the history of clinical data management and the digital transformation of clinical data.
History Of Clinical Data Management
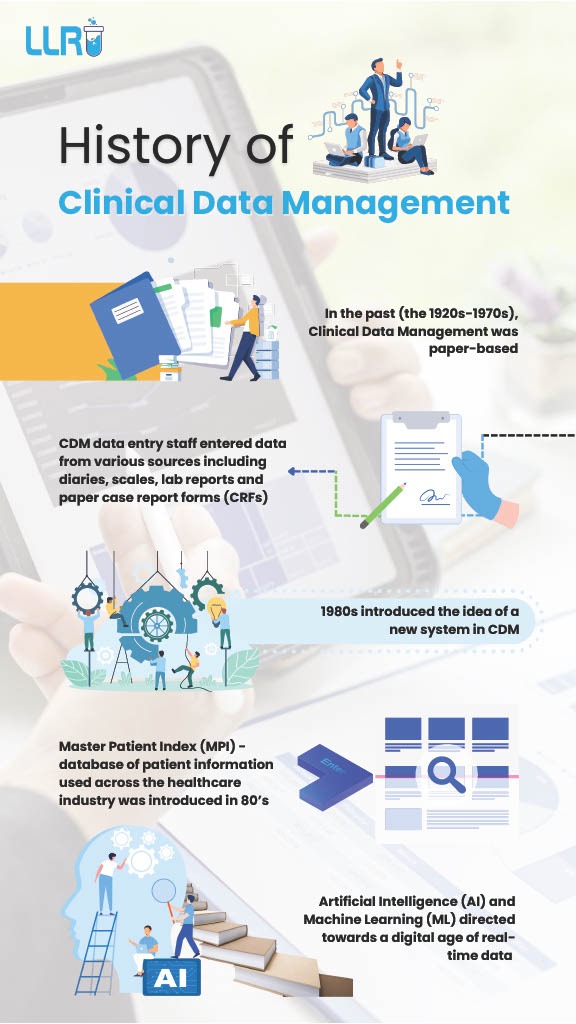
In its infancy, clinical data management relied heavily on manual processes and paper-based documentation – and yes, that means an abundance of papers. The emphasis was on meticulous record-keeping and data accuracy, because that had to be the case or else, it would just be a whole mess.
With the advent of computers in the 1970s, CDM began its transformation towards digitalization. This shift enabled faster data processing, improved data quality, and enhanced efficiency in clinical trials. And the 1990s saw the emergence of specialized software for CDM, facilitating data entry, validation, and reporting. These advancements streamlined processes and reduced the risk of errors, marking a pivotal moment in history of clinical data management.
Let’s take a step-by-step look at the elaborate and intriguing history of clinical data management:
Early beginnings
1960s-1970s: The advent of clinical trials
- Manual data collection: In the early days, clinical trial data were collected manually on paper forms.
- Basic data management: Data management was rudimentary, with simple storage and basic analysis performed manually or using basic software.
1980s: Introduction of computers
- Computerization: The introduction of computers revolutionized data management. Electronic data capture (EDC) systems began to emerge.
- Database management systems: The use of database management systems (DBMS) allowed for more efficient data storage and retrieval.
Clinical Data Management Modernization
As medical research expanded globally, so did the need for more robust CDM systems. Clinical data management modernization efforts focused on integrating data from various sources, including electronic health records (EHRs) and wearable devices. This innovative integration allowed for real-time data capture and monitoring, enhancing decision-making and accelerating clinical trial timelines.
Today, cloud computing has revolutionized Clinical Data Management by offering scalable solutions for data storage and analysis. Cloud-based platforms provide secure access to large datasets, enabling collaboration across geographies and facilitating regulatory compliance – a reflection of the Clinical data management modernization.
2010s: Advanced technologies
- Big data and analytics: The integration of big data and advanced analytics enabled more sophisticated data analysis and insights.
- Cloud computing: Cloud-based CDMS offered scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): The integration of EHRs with CDMS streamlined data collection and improved data accuracy.
2020s: Digital transformation
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are transforming data management by automating complex tasks and identifying patterns.
- Blockchain technology: Blockchain ensures data integrity and security through decentralized and tamper-proof records.
- Remote monitoring: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote monitoring technologies, allowing for real-time data collection and analysis.
Digital Transformation Clinical Data: The Future of Clinical Data Management
Digital transformation in CDM has paved the way for innovative approaches like predictive analytics and artificial intelligence (AI). These technologies automate data processing, identify trends, and predict outcomes with unprecedented accuracy. Moreover, AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data rapidly, offering insights that were previously inaccessible.
Moreover, mobile health (mHealth) applications and telemedicine have expanded data collection capabilities beyond traditional clinical settings, a primary element in clinical research training. Patients can now participate in trials remotely, contributing data through mobile apps and connected devices.

- Mobile health (mHealth): Mobile devices and wearables enable real-time data collection, enhancing patient engagement and data accuracy.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology ensures data security and transparency, mitigating risks associated with data tampering and unauthorized access.
- Virtual trials: Virtual and decentralized trials leverage telemedicine and digital tools, expanding patient access and reducing trial costs and timelines.
- Real-world evidence (RWE): RWEs studies are increasingly used in healthcare decision-making because they represent real-world drug usage and safety concerns, providing real-time patient monitoring.
- Decentralized and hybrid trials: CDM will likely be shaped by trials involving remote recruitment and patient monitoring. Health data collection from wearable devices like mobile phones, smartwatches, and telemedicine platforms necessitates a centralized, cloud-based system for data collection and integration.
On A Final Note…
The history of Clinical Data Management reflects a journey of continuous improvement and innovation. From manual data collection to advanced digital solutions, CDM has evolved to meet the growing demands of clinical research.
When we look at it, the journey of CDM reflects a dynamic interplay of innovation, regulation, and patient-centricity, shaping the future of medical research and healthcare delivery worldwide.
To know more about such interesting facts, visit us at LLRI here!

