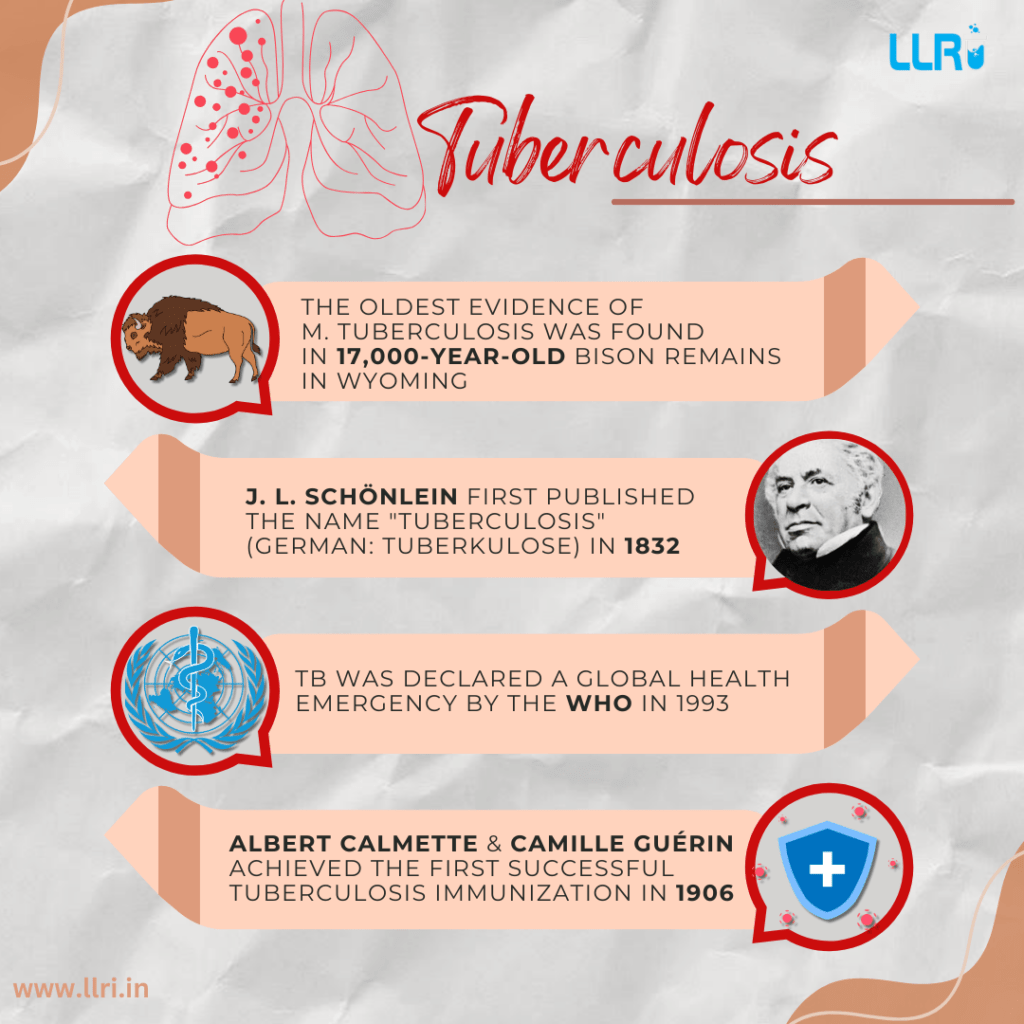
Evolution Of Tuberculosis Treatment: Did you know that Tuberculosis is one of the oldest diseases in the history of mankind? Yes, there is evidence of tubercular decay reported in some Egyptian mummies from 3000-2400 BC.
In India, tuberculosis causes about 220,000 deaths every year – that is, two deaths occurring every three minutes: with more than 40% of the population carrying the disease. Imagine the horror!
Tuberculosis (TB) has been a significant global health issue for centuries. The evolution of tuberculosis treatment reveals how medical science has transformed from rudimentary approaches to sophisticated antibiotics – and that is what we will be exploring in this blog – the journey from early treatments to current options, focusing on the early cure for tuberculosis and the availability of tuberculosis antibiotics today.
Evolution Of Tuberculosis Treatment: Overview
The evolution of tuberculosis treatment is surrounded by several major milestones, from ancient herbal remedies to the powerful antibiotics; here’s a summary of the journey:
- Ancient times: Reliance on herbal remedies and non-specific treatments.
- 19th century: Use of sanatoria for rest and fresh air.
- Early 20th century: Introduction of surgical methods.
- 1940s and beyond: Discovery and use of antibiotics, including streptomycin, isoniazid, and rifampin, leading to more effective and targeted treatments.
Early Cure for Tuberculosis: A Historical Perspective
Tuberculosis treatment has undergone several changes since the disease was first described. To understand the evolution, let’s look at the history of tuberculosis treatment:
| Era | Treatment | Details |
| Ancient Times | Rest and fresh air | Ancient societies believed in the healing power of rest and fresh air. |
| 19th Century | Sanatoriums | Patients were sent to sanatoriums where rest and a healthy diet were prescribed. |
| 1920s | Introduction of tuberculin test | This diagnostic test, developed by Robert Koch, was a major step in understanding TB. |
| 1940s | Discovery of streptomycin | The first antibiotic used specifically to treat tuberculosis, revolutionizing the cure for tuberculosis history. |
| 1950s | Combination therapy | Use of multiple antibiotics like Isoniazid and Rifampicin to prevent resistance. |
| Present Day | Modern antibiotics and DOTS | Directly Observed Treatment Short-course (DOTS) ensures adherence to treatment with a combination of antibiotics. |
In the early days, the early cure for tuberculosis was more about managing symptoms rather than a true cure. Sanatoriums were the primary method of treatment, where patients would rest in a controlled environment.
It was believed by the experts of the yesteryears was that fresh air and rest could help the body fight off the disease. This approach, while beneficial, was not a cure but rather a way to improve the patient’s condition and manage symptoms.
Evolution Of Tuberculosis Treatment
The evolution of tuberculosis treatment took a leap with the discovery of antibiotics. Before the 20th century, tuberculosis was a major cause of death, and treatments were limited to supportive care.
When did the antibiotic revolution begin?
The real breakthrough came in the 1940s with the discovery of Streptomycin by Selman Waksman. This was the first effective antibiotic against TB and marked a new era in the evolution of tuberculosis treatment. Following this, other antibiotics such as Isoniazid and Rifampicin were introduced, leading to more effective treatments.
Combination therapy became the standard practice in the 1950s to prevent the development of drug-resistant strains of TB. This method uses multiple antibiotics to increase the effectiveness of treatment and reduce the risk of resistance. The cure for tuberculosis history was forever changed with these advancements, turning what was once a fatal disease into a manageable condition.
The discovery of antibiotics really revolutionized the evolution of tuberculosis treatment. Before antibiotics, treatments were limited to surgery and supportive care. Here’s a look at how antibiotics changed the landscape:
1. Streptomycin: Discovered in the 1940s, streptomycin was the first antibiotic that showed effectiveness against TB. This discovery marked the beginning of the modern era in TB treatment and highlighted the importance of antibiotics in the evolution of tuberculosis treatment.
2. Isoniazid and rifampin: The introduction of isoniazid in the 1950s and rifampin in the 1960s further advanced TB treatment. These antibiotics, used in combination, significantly improved treatment outcomes and reduced the duration of therapy.
3. Multi-drug regimens: In the late 20th century, the use of multi-drug regimens became standard practice. This approach helps to prevent the development of drug-resistant strains of TB and improves overall treatment efficacy.
Tuberculosis Antibiotic Availability: Are Tuberculosis Antibiotics Available?
Today, the evolution of tuberculosis treatment continues with the availability of various antibiotics. Modern TB treatment typically involves a combination of drugs taken over several months. The most commonly used antibiotics include the following:
- Isoniazids
- Rifampicin
- Ethambutol
- Pyrazinamide
Directly Observed Treatment Short-course (DOTS) is a globally recommended expert strategy to ensure that patients complete their treatment regimen. DOTS involves regular monitoring by healthcare providers to ensure adherence to the prescribed antibiotic regimen, thus preventing the development of drug-resistant TB.
Cure For Tuberculosis: History
The evolution of tuberculosis treatment took a major leap with the discovery of antibiotics. Here’s a chronological look at the major milestones in the history of tuberculosis treatment:
| Year | Milestone |
| 1882 | Robert Koch discovers the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. |
| 1943 | Streptomycin, the first effective tuberculosis antibiotic, is discovered. |
| 1952 | Introduction of Rifampin, which significantly improves treatment outcomes. |
| 1960s | The development of combination therapy reduces the risk of drug resistance. |
| 1980s | Directly Observed Therapy (DOTS) is introduced to enhance treatment adherence. |
| 1990s | Introduction of newer drugs like Fluoroquinolones for multidrug-resistant TB. |
| 2000s | Bedaquiline, a new class of TB antibiotic, is approved for use in multidrug-resistant cases. |
On A Final Note…
The evolution of tuberculosis treatment from early supportive care to advanced antibiotic therapies represents a significant achievement in medical science. The early cure for tuberculosis was rudimentary at best, but the development of antibiotics marked a turning point in treating this once-deadly disease.
With the continued availability of effective tuberculosis antibiotics, TB is now a manageable condition rather than a fatal illness.

