Have you ever submitted a medical claim only to see it bounced back for “coding error,” even when the procedure codes looked right?
Modifiers in medical coding provide that extra layer of detail needed to tell the full story of patient care. These simple two-character additions to CPT or HCPCS codes clarify special circumstances, like procedure location or repetition, helping insurers process claims smoothly.
In India’s growing healthcare sector, where digital billing under schemes like Ayushman Bharat demands precision, mastering these tools cuts denials and speeds up payments.
Table of Contents
What are Modifiers in Medical Coding?
Modifiers in Medical Coding are two-digit codes added to CPT or HCPCS codes to give extra information about a medical procedure or service without changing the main code. It signals variations in service delivery without changing the code’s basic meaning, such as whether a surgery happened on both sides of the body.
Coders in Indian hospitals use them daily to meet IRDA and NABH standards. For better billing knowledge, see our related post: What Is Modifier In Medical Billing: List of Modifiers, Types, Uses, Cheat Sheet.
Basically, modifiers explain how, why, or under what condition a procedure was performed.
Why does this matter to you? Without modifiers, payers might bundle services wrongly, slashing reimbursements by up to 30%.
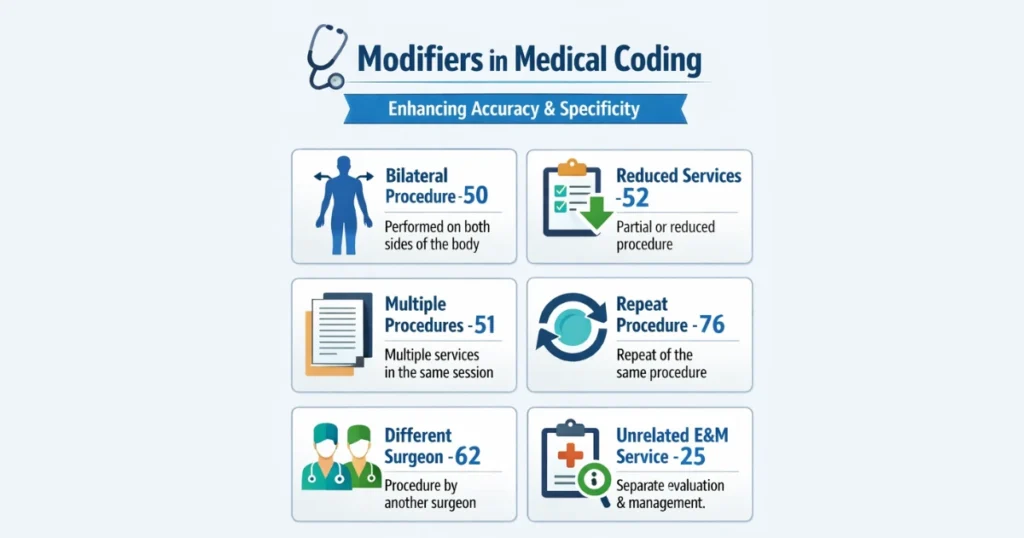
Types of Modifiers
Modifiers split into clear categories for easy application. CPT Level I modifiers are numeric and cover physician services, while HCPCS Level II are alphanumeric for items like ambulance rides or drugs.
- Pricing modifiers tweak payment amounts, such as those for multiple procedures.
- Informational modifiers add context, like reduced services.
- NCCI-associated modifiers override bundling rules from the US National Correct Coding Initiative, now influencing global standards.
In India, these align with CGHS guidelines, where modifier choice affects scheme payouts directly.
Modifiers List in Medical Coding
Need a quick modifiers list in medical coding? This table lists the most used ones, with practical notes pulled from standard references.
| Modifier | Description | Uses |
| -25 | Significant, separate E/M service same day | Office visit (99213-25) plus X-ray |
| -50 | Bilateral procedure | Hernia repair on both sides (49505-50) |
| -59 | Distinct procedural service | Two lesions excised separately (11402, 11102-59) |
| -76 | Repeat procedure by same physician | Repeat ECG same day (93000-76) |
| -24 | Unrelated E/M in post-op period | Post-surgery visit for new rash (99213-24) |
| LT/RT | Left/right side | Knee injection left (J1040-LT) |
AAPC notes, “Correct modifier placement boosts first-pass claim acceptance rates.” Keep this handy for your coding desk.
Essential and Nonessential Modifiers in Medical Coding
Essential and nonessential modifiers in medical coding shine in ICD-10-CM indexing.
- Essential modifiers, listed as indented subterms, must match patient records to pick the exact diagnosis code – think “chronic” under kidney disease.
- Nonessential modifiers appear in parentheses and provide optional detail; their absence does not shift the code. For instance, “due to” might clarify aetiology without mandating a code change.
ICD-10 guidelines clarify: “Nonessential modifiers do not affect code assignment unless specified otherwise.” Indian coders rely on this for AB-PMJAY claims, ensuring NABH audits pass smoothly.

Modifiers in Medical Coding: Examples
Here are some examples for your easy understanding:
Example 1: Modifier 25 (Significant, separate E/M service)
Doctor evaluates asthma (99214-25) then administers nebulisation (94640). The -25 flags the evaluation as distinct.
Example 2: Modifier 50 (Bilateral procedure)
Bilateral tubal ligation (58615-50) bills at 150% rate since both sides count as one unit with adjustment.
Example 3: Modifier 25 (Significant, separate E/M service)
Incision/drainage (10060) and wound check (99212-25) same visit – -25 unbundles them.
Example 4: Modifier 59 (Distinct procedural service)
Patient undergoes skin lesion excision on the arm (11403) and separately, a wart removal on the foot (17110) during the same session. Code as 11403, 17110-59. The -59 indicates the services occurred at distinct anatomic sites, bypassing NCCI bundling edits
Example 5: Modifier 76 (Repeat procedure by same physician)
ECG performed for chest pain (93005), then repeated later the same day due to ongoing symptoms (93005-76). The -76 flags the repeat as medically necessary, allowing separate billing.

What To Avoid?
Common slip-ups include slapping -59 on everything – try specific XE (separate encounter) first. Always sequence pricing modifiers before others, like -50 then -59.
Quick tips:
- Check payer-specific rules; Medicare skips -51.
- Document clearly – “separate incision site, 2 cm apart.”
- Review NCCI edits quarterly for updates.
- For Indian practices, cross-check with IRDA circulars to dodge denials.
On A Final Note…
With India’s health insurance market hitting 1 lakh crore, modifiers drive revenue cycle efficiency. Accurate use drops rejection rates, vital for hospitals under Ayushman Bharat. Training coders here pays off fast.
FAQs
What is modifier in medical coding?
A code added to CPT/HCPCS to note service variations like site or repeats.
What are essential and nonessential modifiers in medical coding?
Essential: Required subterms for code choice. Nonessential: Parenthetical clarifiers, optional.
Can you share modifiers list in medical coding?
Yes – top ones: -25, -50, -59, LT/RT (see table).
Show modifiers in medical coding with examples?
-25: E/M + procedure. -50: Both sides bilateral.