RCM Cycle in Medical Billing: Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) plays a major role in medical billing, helping healthcare providers receive timely payments for their services. Without an efficient RCM cycle, hospitals and clinics may face financial losses. But what is RCM cycle in medical billing, and how does it work?
This blog will break down the RCM cycle steps in medical billing, explain the RCM cycle flow chart, and explore its impact on healthcare revenue. Whether you’re a medical billing professional, a student at a clinical research training center, or simply curious about the process, this blog will take you all through it!
What is RCM Cycle in Medical Billing?
The RCM cycle in medical billing is the financial process healthcare providers use to track patient care from registration to the final payment. It involves several steps, making sure that providers get paid for their services while following insurance policies and regulations.

Why is the RCM Cycle Important?
- Helps with timely payments – Without a proper RCM cycle flow chart, billing errors can delay payments.
- Reduces claim denials – A well-structured RCM cycle steps in medical billing process minimizes rejected claims.
- Improves patient satisfaction – Efficient billing leads to better financial transparency for patients.
- Supports hospital operations – Revenue from RCM helps hospitals and clinics function smoothly.
A well-managed RCM cycle in medical billing can increase revenue collection efficiency and reduce claim rejections, leading to a more sustainable healthcare system.
RCM Cycle Steps in Medical Billing
The RCM cycle in medical billing follows a structured process. Let’s look at the key steps:
1. Patient Registration
The first step is collecting patient details, including personal and insurance information. Any errors in this step can cause claim rejections later.
2. Insurance Eligibility Verification
Before providing services, the hospital must verify whether the patient’s insurance covers the treatment. This prevents claim denials.
3. Medical Coding & Charge Capture
After the patient receives treatment, healthcare providers document the services using standardized codes (ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS). Accurate coding helps in correct billing.
4. Claim Submission
The hospital submits a claim to the insurance company for reimbursement. A small mistake can lead to claim rejection.
5. Payment Processing & Denial Management
If the claim is approved, payment is processed. If denied, the provider must correct errors and resubmit.
6. Patient Billing & Collection
After insurance payment, the patient receives the remaining balance bill.
7. Reporting & Analysis
Hospitals analyse RCM performance to find areas for improvement and reduce claim rejections.
RCM Cycle Flow Chart
An RCM cycle flow chart visually represents the entire billing process. Here’s a simplified version:
- Patient Registration → 2. Insurance Verification → 3. Medical Coding → 4. Claim Submission → 5. Payment Processing → 6. Patient Billing → 7. Performance Analysis
Here is an RCM cycle flow chart for your understanding:
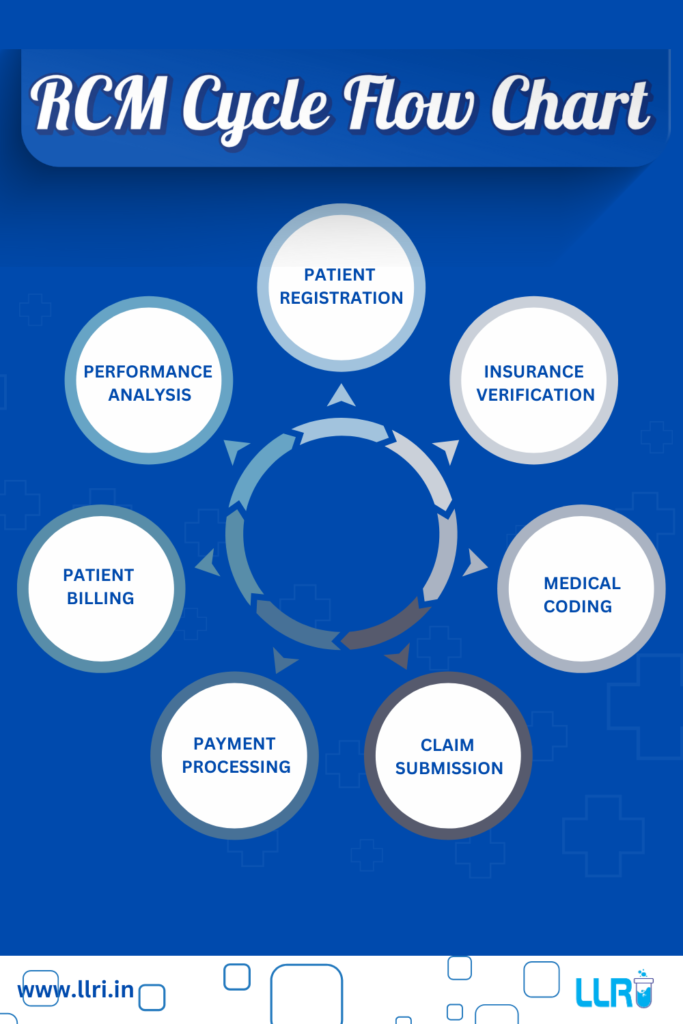
The RCM cycle consists of multiple interconnected steps, from patient registration to performance analysis. Below is a detailed breakdown of each step in the RCM cycle:
1. Patient Registration
The revenue cycle begins with patient registration. During this step:
- The healthcare provider collects the patient’s personal details, including name, date of birth, contact information, and medical history.
- Insurance details, including policy number and payer information, are recorded.
- Demographic data is verified to ensure accuracy and prevent claim denials.
Why is this important? Incorrect or incomplete patient information can lead to claim rejections, delaying the reimbursement process.
2. Insurance Verification
Before any services are provided, the healthcare provider verifies the patient’s insurance coverage. This step includes:
- Checking eligibility and coverage limits.
- Confirming co-payments, deductibles, and prior authorization requirements.
- Identifying services that require pre-approval from the insurance company.
Why is this important? Failure to verify insurance details can result in denied claims or unexpected out-of-pocket costs for patients.
3. Medical Coding
Once a patient receives treatment, medical coders translate diagnoses, procedures, and treatments into standardized codes, such as:
- ICD-10 codes (for diagnoses).
- CPT and HCPCS codes (for procedures and services).
Coders must follow strict compliance guidelines to avoid claim denials and ensure correct reimbursement.
Why is this important? Accurate coding is essential for maximizing reimbursement and minimizing claim rejections due to errors.
4. Claim Submission
After coding, the healthcare provider submits the claim to the insurance company for payment. This step involves:
- Reviewing claims for accuracy before submission.
- Sending claims electronically via clearinghouses for faster processing.
- Ensuring compliance with payer-specific guidelines.
Why is this important? Incorrect or incomplete claims can lead to delays, rejections, or denials, impacting cash flow.

5. Payment Processing
Once the insurance company receives the claim, they:
- Review the claim details and cross-check them against the patient’s coverage.
- Approve or deny payment based on policy terms and coding accuracy.
- Issue an Explanation of Benefits (EOB) to both the provider and the patient.
If the claim is denied, the provider may need to correct errors and resubmit it.
Why is this important? Quick and accurate payment processing ensures steady revenue for healthcare providers.
6. Patient Billing
After the insurance company processes the claim, any remaining balance is billed to the patient. This includes:
- Co-pays, deductibles, or uncovered services.
- Sending invoices and following up on unpaid balances.
- Offering payment plans or financial assistance if necessary.
Why is this important? Clear and timely patient billing improves collections and reduces bad debt.
7. Performance Analysis
The final step involves evaluating the efficiency of the revenue cycle. This step includes:
- Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) like denial rates, days in accounts receivable, and reimbursement timelines.
- Identifying trends in claim denials or payment delays.
- Implementing strategies to optimize revenue cycle performance.
Why is this important? Continuous analysis and improvement of the RCM process help healthcare providers enhance cash flow and operational efficiency.
An optimized Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) process ensures financial stability for healthcare providers while improving patient satisfaction. Each step, from patient registration to performance analysis, plays a critical role in streamlining operations and maximizing reimbursements.
Want to improve your RCM process? Focus on automation, accurate coding, and proactive claim monitoring!
Challenges in the RCM Cycle in Medical Billing
Managing the RCM cycle in medical billing is not always easy. Here are some common challenges:
- Claim denials – Incorrect patient details, coding errors, or eligibility issues can lead to rejections.
- Delayed payments – Processing delays from insurance companies or incorrect claim submissions can impact cash flow.
- Regulatory changes – Medical billing regulations keep evolving, requiring constant updates.
- Patient payment collection – Many patients struggle with out-of-pocket expenses, leading to unpaid bills.
According to a 2023 report by Healthcare Financial Management Association (HFMA), more than 30% of hospital claims face initial denials due to missing or incorrect information.
How Can Hospitals Improve RCM Cycle in Medical Billing?
To keep billing and revenue collection smooth, healthcare providers should follow best practices like:
- Automating RCM processes – Using software to verify insurance, track claims, and reduce human errors.
- Training medical billing staff – A well-trained team helps with accurate coding and claims management.
- Regular audits – Checking RCM performance helps identify errors before they become major issues.
- Focusing on patient communication – Clear billing explanations help patients understand their financial responsibilities.
A study by IKS Health has found that hospitals using AI-based RCM solutions saw a 20% reduction in claim denials.
The Role of Clinical Research in Medical Billing
Medical billing is closely linked to clinical research. Research institutions like Learning Labb Research Institute (LLRI) play a key role in developing better healthcare practices, including improving RCM strategies.
If you’re interested in learning more, consider enrolling in a clinical research course at a clinical research training center.
Benefits of a Clinical Research Course for RCM Professionals
- Helps understand the connection between medical billing and clinical trials
- Improves knowledge of insurance policies and regulations
- Enhances skills in medical documentation and coding

Many top institutes offer specialized programs, such as:
- Best Institute for PG Diploma in Clinical Research – Ideal for professionals looking to expand their healthcare expertise.
- Clinical Research Training Center Programs – Focused on real-world applications of clinical research.
- Clinical Research Course Fees – Vary based on location and duration, but many institutes offer flexible payment plans.
By combining RCM cycle in medical billing knowledge with clinical research training, healthcare professionals can improve both patient care and financial efficiency.
On A Final Note…
The RCM cycle in medical billing is an important aspectof the healthcare industry. From patient registration to final payment, every step plays a role in maintaining financial stability.
If you’re looking to build your career in medical billing, consider taking a clinical research course at a clinical research training center. Institutions like Learning Labb Research Institute (LLRI) offer specialized programs that can help professionals master the complexities of medical billing.
Got questions about the RCM cycle steps in medical billing or the RCM cycle flow chart? DM us NOW!

