What is Genetic Engineering: Genetic engineering is one of the most fascinating fields of modern science. It has changed the way we look at life, health, agriculture, and even the environment.
But what is genetic engineering? How is it done, and why is it so important today?
In this blog, we will explain everything about genetic engineering -its meaning, applications, purpose, steps and everything you need to know!
What is Genetic Engineering?
Genetic engineering is the process of directly changing or modifying the DNA of an organism to achieve desired traits. It means taking genes from one organism and inserting them into another to make changes that do not occur naturally. This technology is also known as recombinant DNA technology.
As Nobel laureate Paul Berg, who is known as the “father of genetic engineering,” once said: “With genetic engineering, we can do things nature never allowed before.” This statement shows the true power of this science.
If you are wondering, what is genetic engineering? The answer is simple: it is a scientific method that allows humans to design or re-design life.
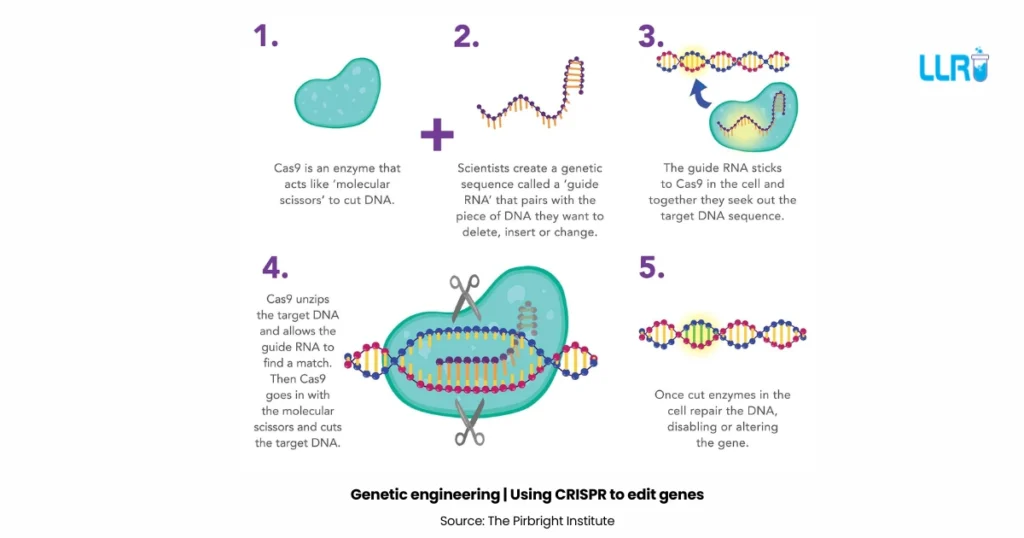
Principles of Genetic Engineering
To understand how genetic engineering works, it is important to know its basic principles. The principles of genetic engineering are:
- Identification of the target gene: First, the gene responsible for a particular trait is identified.
- Isolation of the gene: The gene of interest is separated using special enzymes.
- Insertion into a vector: The isolated gene is then inserted into a vector for transfer.
- Introduction into host organism: The vector carrying the gene is introduced into the host.
- Expression of gene: The host organism shows the desired trait.
This step-by-step method forms the backbone of all genetic engineering processes.
Tools of Genetic Engineering
No science is possible without tools. The tools of genetic engineering include:
- Restriction enzymes: Act like scissors to cut DNA at specific sites.
- Ligases: Help in joining DNA fragments.
- Vectors: Used to carry the desired gene into the host cell.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): Helps in making many copies of a gene.
- DNA sequencing techniques: Used to read the genetic code.
These tools make it possible to work with the smallest unit of life – DNA.
Read More: Regulation of Gene Expression: Mechanisms, Types Explained
Vectors Used in Genetic Engineering
Vectors are like delivery vehicles in genetic engineering. Without them, the transfer of genes is not possible. Some common vectors used in genetic engineering are:
- Plasmids: Small circular DNA found in bacteria.
- Bacteriophages: Viruses that infect bacteria.
- Cosmids: Hybrid vectors that carry larger DNA fragments.
- Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs): Used for carrying very large DNA sequences.
Each vector has its own advantage depending on the type of experiment.
Steps of Genetic Engineering
If you are curious about how scientists actually do it, here are the main steps of genetic engineering:
- Selection of the gene of interest.
- Cutting the DNA with restriction enzymes.
- Inserting the gene into a vector.
- Transferring the vector into the host organism.
- Screening to check successful modification.
- Expression of the new gene.
This process looks simple on paper but requires very advanced laboratories and trained professionals.
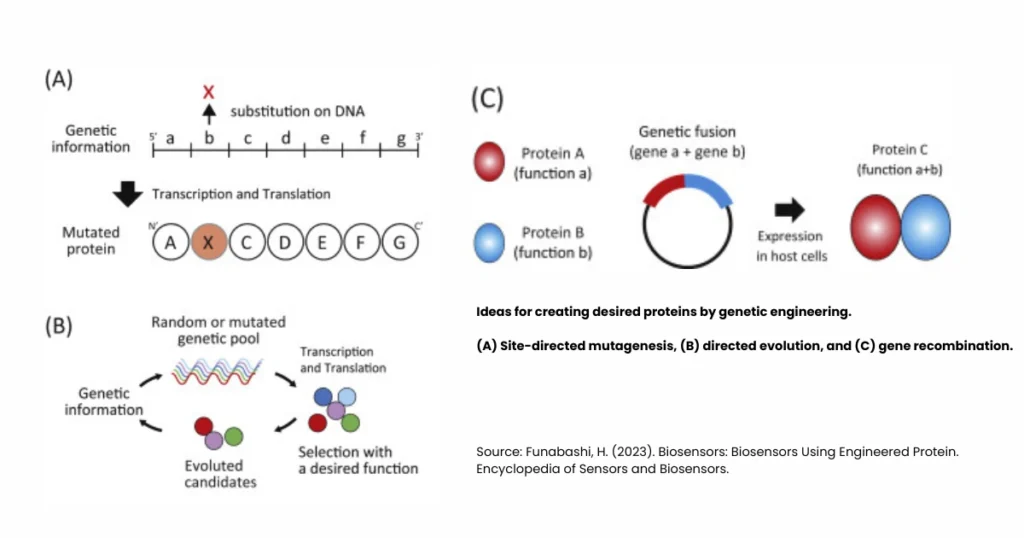
What is the Purpose of Genetic Engineering?
Now you may ask, what is the purpose of genetic engineering? The main purpose is to solve real-world problems. Whether it is food production, healthcare, or environmental protection, genetic engineering gives us solutions.
Some main purposes are:
- To produce medicines like insulin and vaccines.
- To create crops resistant to pests, drought, or diseases.
- To improve the nutrition level of food.
- To cure genetic disorders.
- To develop eco-friendly industrial processes.
Application of Genetic Engineering
The application of genetic engineering is very wide. It has touched almost every field of life, such as;
- Medicine: Used to produce life-saving drugs, vaccines, and even gene therapy treatments. In India, the use of CRISPR-based therapies for rare diseases is gaining attention. In 2023, researchers reported trials on CRISPR gene-editing for blood disorders like sickle cell anaemia.
- Agriculture: Development of genetically modified crops (GMOs) that grow faster and resist pests. According to the Indian Ministry of Agriculture, Bt cotton (a genetically modified crop) covers over 90% of India’s cotton-growing area, making the country one of the largest producers in the world.
- Industry: Microorganisms are engineered to produce biofuels, enzymes, and other useful products.
- Environment: Bacteria are designed to clean up oil spills and degrade plastic. A 2022 Indian study highlighted engineered microbes that can break down single-use plastics more efficiently.
As a result, the uses of genetic engineering are unlimited and expanding every day.
Types of Genetic Engineering
There are different types of genetic engineering depending on the target area:
- Analytical genetic engineering: Understanding genetic information.
- Applied genetic engineering: Practical applications like crop improvement.
- Chemical genetic engineering: Altering genetic material using chemicals.
Each type has its importance in research and industry.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Genetic Engineering
Like any technology, genetic engineering has two sides. Let us look at the advantages and disadvantages of genetic engineering.
Advantages:
- Helps in producing medicines quickly.
- Improves crop yield and food security.
- Cures or reduces genetic disorders.
- Protects the environment with eco-friendly solutions.
Disadvantages:
- Ethical concerns about “playing with life.”
- Risk of genetic mutations.
- Expensive process not available everywhere.
- Fear of genetically modified food in society.
The debate is still ongoing, but the benefits often outweigh the risks when used responsibly.
Importance of Genetic Engineering
Why is this field so important today? The importance of genetic engineering can be explained through its impact:
- It saves lives by producing drugs like insulin.
- It feeds millions by increasing food production.
- It fights climate change by supporting sustainable practices.
- It gives scientists tools to understand life better.
In short, without genetic engineering, many modern medical and agricultural solutions would not exist.
Scope of Genetic Engineering: What Is the Use?
In India, the scope of genetic engineering is growing rapidly. According to industry reports, the Indian biotechnology sector is expected to reach USD 150 billion by 2025, and genetic engineering is one of its driving forces. With industries in pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and research expanding, the demand for skilled professionals is increasing.
For students looking at future-ready careers, genetic engineering is a strong choice.
Career Opportunities in Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineers can work in:
- Pharmaceutical companies.
- Research and development (R&D) labs.
- Agricultural biotechnology firms.
- Healthcare and diagnostic labs.
As one industry expert says: “The 21st century is the century of biology, and genetic engineering will be at its centre.”

Future of Genetic Engineering
The future is exciting. Genetic engineering will play a major role in personalized medicine, artificial organs, and sustainable farming. With technologies like CRISPR becoming popular, the possibilities are endless.
On A Final Note…
So, what is genetic engineering? It is the science of changing genes to improve life. Its principles, tools, applications, and uses have already reshaped the world. The scope of genetic engineering in India and abroad is huge, and the demand for skilled professionals will only grow.
If you are a student or a professional asking yourself – Should I learn genetic engineering? The answer is yes. Because tomorrow’s science and tomorrow’s jobs will be designed at the DNA level.
FAQs
Q1. What is genetic engineering in simple words?
It is the process of changing or modifying DNA to create desired traits in organisms.
Q2. What are the main tools of genetic engineering?
The main tools include restriction enzymes, ligases, vectors, PCR, and sequencing techniques.
Q3. What is the purpose of genetic engineering in medicine?
The purpose is to create medicines, vaccines, and therapies that can save lives and treat genetic disorders.
Q4. What are the applications of genetic engineering in agriculture?
It is used to make crops resistant to pests, drought, and diseases, and to improve yield and nutrition. In India, Bt cotton is a widely used genetically engineered crop.
Q5. What is the scope of genetic engineering in India?
The scope is high, with growing opportunities in pharmaceutical companies, research institutes, and agricultural biotechnology firms. Institutes like LLRI provide practical training and job support in this field.
Q6. What are the advantages and disadvantages of genetic engineering?
Advantages include medical benefits, improved crops, and environmental solutions. Disadvantages include ethical concerns, risks of mutations, and public fear of GM foods.
Q7. What is the latest trend in genetic engineering?
The latest trend is the use of CRISPR-Cas9 technology, which allows precise editing of genes. Indian researchers are actively working on CRISPR-based solutions for healthcare and agriculture.