What Are The 4 Phases Of Clinical Trials: Clinical trials are absolutely essential to the progress of modern medicine, serving as the definitive pathway for developing groundbreaking, life-saving drugs and therapies.
But what exactly are the 4 phases of clinical trials, and how do they work?
Clinical Trials Definition and Phases
Clinical trials are systematic studies conducted to evaluate the safety, efficacy, and potential side effects of new drugs, devices, or treatments in humans. These trials bridge the gap between laboratory research and public use, ensuring that a medical product is safe and effective before being marketed.
As the clinical trials phases flow chart illustrates below, these trials progress through four well-defined stages, each with unique objectives. Together, these phases create a framework for evaluating new interventions.

The 4 Phases of Clinical Trials
Each phase in a clinical trial build on the previous one, gathering more information about the treatment in question.
Phase I: Assessing Safety and Dosage
Phase I is the first step in human testing. This phase usually involves a small group of 20-100 healthy volunteers or patients and focuses on the following objectives:
- Determining the safety of the drug
- Establishing the appropriate dosage
- Identifying potential side effects
At this stage, researchers aim to answer a critical question: “Is this treatment safe for humans?” According to the Indian Society for Clinical Research, less than 10% of drugs pass Phase I due to safety concerns.
Simply put, phase I is like a first handshake with a new treatment, testing its compatibility with the human body.
Phase II: Evaluating Effectiveness
Once safety is established, Phase II expands the study to a larger group of patients, usually between 100-300 individuals. Phase II trials are the bridge between promise and proof.
The goals include the following:
- Assessing the effectiveness of the treatment
- Further evaluating safety
- Identifying optimal treatment protocols
Here, participants are often individuals with the condition the drug aims to treat. For example, a Phase II trial for a new diabetes drug would involve diabetic patients.
Phase III: Confirming Effectiveness and Monitoring Adverse Reactions
Phase III trials are central to the whole process. They involve thousands of participants across multiple sites to confirm the treatment’s efficacy on a large scale. This phase includes:
- Comparing the new treatment with standard therapies
- Monitoring adverse reactions in diverse populations
- Finalising safety and efficacy data for regulatory approval
For instance, the recent COVID-19 vaccine trials relied heavily on Phase III data to gain emergency use authorization.
This phase is important for gaining approval from regulatory bodies like the FDA or the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI). Many clinical research training programs teach aspiring professionals how to design and monitor Phase III trials.
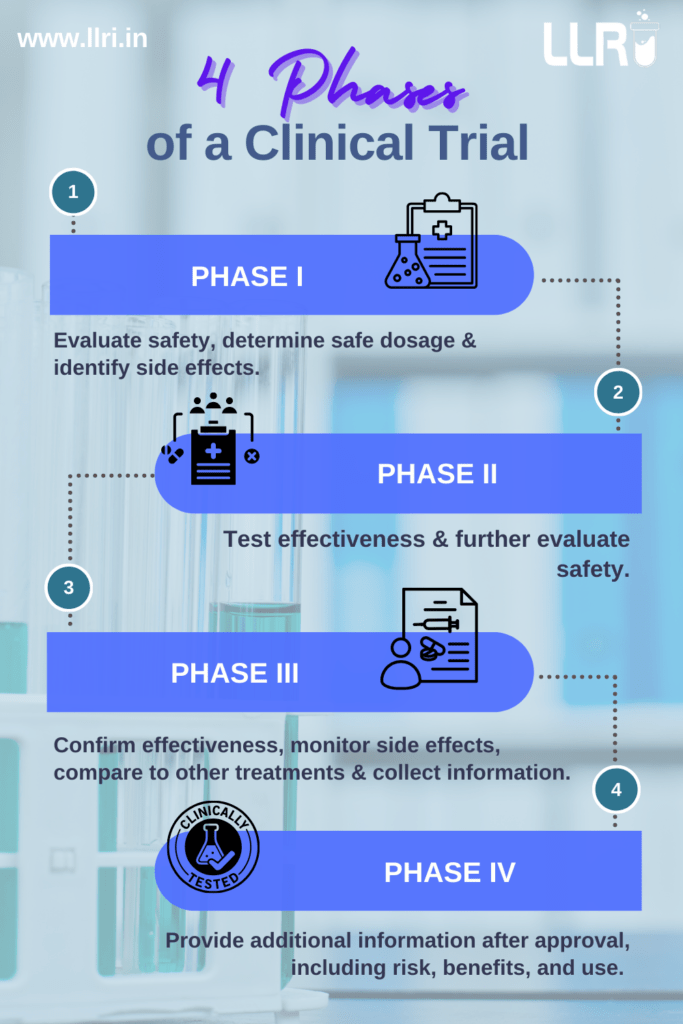
Phase IV: Post-Marketing Surveillance
The journey doesn’t end with regulatory approval. Phase IV trials, often called post-marketing studies, continue after the treatment is available to the public. The goals of this phase are:
- Monitoring long-term safety
- Evaluating effectiveness in real-world conditions
- Detecting rare side effects
For example, Phase IV trials for a new painkiller might uncover a rare side effect that occurs only after prolonged use.
Why Are the Various Phases of Clinical Trials Important?
Each phase plays a distinct role in the development process. Together, they assure that new treatments are:
- Safe for human use
- Effective in treating specific conditions
- Minimally harmful with manageable side effects
Without the rigorous structure of the different phases of clinical trials, the risks of unsafe or ineffective treatments reaching the public would increase significantly.
Clinical Trials Phases Flow Chart
This chart highlights how each phase builds upon the previous one, creating a robust system for drug development.
| Phase | Participants | Primary Focus |
| Phase I | 20-100 healthy volunteers | Safety and dosage |
| Phase II | 100-300 patients | Effectiveness and side effects |
| Phase III | Thousands of patients | Large-scale testing and comparisons |
| Phase IV | Public users | Long-term safety and effectiveness |
How to Build a Career in Clinical Research?
If the field of clinical research excites you, numerous opportunities await. From clinical research courses to specialised clinical research training, India offers world-class education for aspiring professionals.
Best Institute for PG Diploma in Clinical Research
One of the leading names in this domain is LLRI (Learning Labb Research Institute). Offering industry-focused programs, LLRI has become a preferred clinical research training center for students across the country. Their curriculum covers:
- Fundamentals of the 4 phases of clinical trials
- Designing and managing trials
- Regulatory requirements and ethics
LLRI also provides hands-on training to prepare students for real-world challenges, making it one of the best institutes for PG Diploma in Clinical Research.
Clinical Research Course Fees and Accessibility
Many aspirants worry about the cost of training. Fortunately, institutions like LLRI offer affordable clinical research course fees along with scholarship programs. This makes quality education accessible to a broader audience.
On A Final Note…
The 4 phases of clinical trials form a meticulous process that makes sure that the new treatments are safe and effective for public use. From early-stage safety testing to post-marketing surveillance, each phase plays a vital role in advancing healthcare.
For those aspiring to contribute to this transformative field, pursuing a clinical research course from institutions like LLRI is a step in the right direction. With affordable clinical research course fees and excellent training, you can build a fulfilling career in one of the most impactful industries.
FAQs
-
What are the 4 phases of clinical trials?
The four phases are Phase I (safety and dosage), Phase II (effectiveness), Phase III (large-scale testing), and Phase IV (post-marketing surveillance).
-
What is the purpose of clinical trials?
The goal is to evaluate the safety, efficacy, and long-term effects of new drugs or treatments.
-
How can I become a clinical research professional?
By enrolling in a clinical research course at a reputable clinical research training center, such as LLRI.
-
Are clinical research courses expensive?
The clinical research course fees vary but are generally affordable, with options for scholarships.
-
Which is the best institute for clinical research training in India?
LLRI is highly regarded for its industry-aligned curriculum and hands-on training.

